Challenge 1 : NRF
In this section, we will explore the role and functionality of the NRF in the 5G core network. We’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of its importance and discover how it facilitates service discovery. Additionally, we will delve into the process of configuring the NRF with its parameters.
NRF: The Central Registry for Network Functions
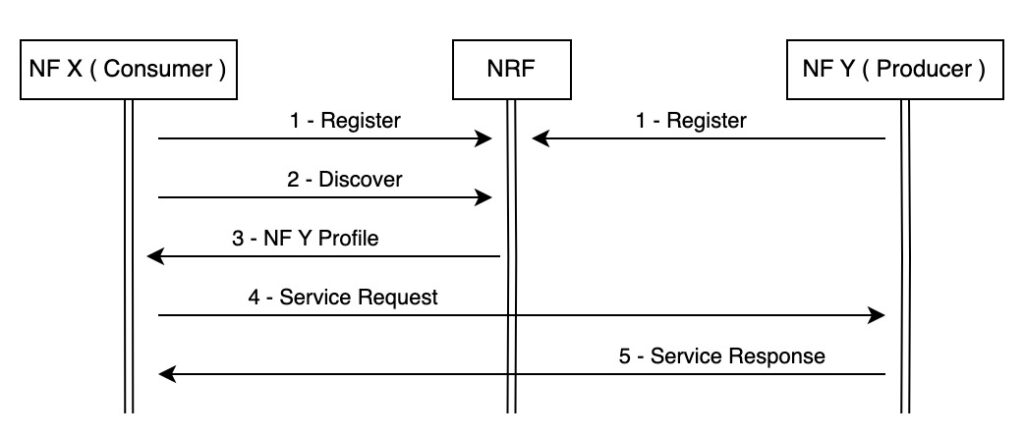
The NRF (Network Repository Function) serves as a central registry in the network, containing information about each Network Function (NF). This information can be shared with any NF whenever necessary.
When introducing a new NF or expanding an existing one, the new NF instance only needs to interact with the NRF. By doing so, it registers its profile and gains visibility into all the NFs that make up the network.
In order to establish their presence within the network, all Network Functions (NFs) are required to register their profiles in the NRF. The NF profile encompasses crucial details such as the supported services, PLMN specifications, IP address and other relevant information.
The following figure present the NRF registration and discovery process:
- PLMN : Public Land Mobile Network Identifier is a combination of MCC ( Mobile Country Code ) and MNC ( Mobile Network Code ). It is a unique value and globally used to identify the mobile network that a user subscribed to.
Example: PLMN = 20893 (MCC = 208, MNC=93)
NRF: Configuration
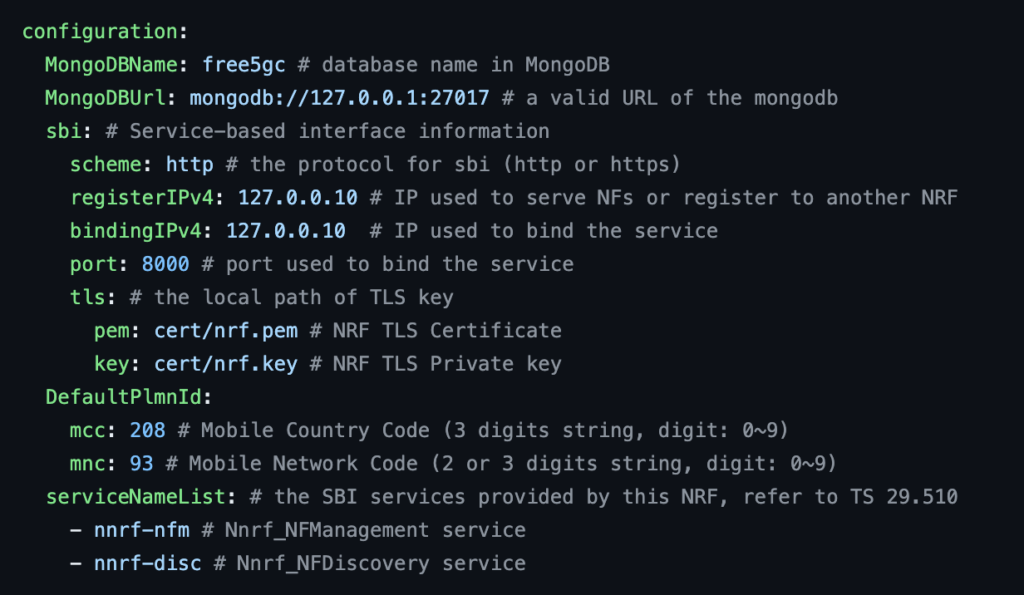
To properly configure the NRF (Network Repository Function), you need to set up the following attributes in the configuration file located at “~/free5gc/config/nrfcfg.yaml”:
- “registerIPv4”: This attribute specifies the IPv4 address used by the NRF for registration purposes. It determines the IP address that other network functions will use to register their profiles with the NRF.
registerIPv4: 127.0.0.10
- “bindingIPv4”: This attribute defines the IPv4 address that the NRF binds to for communication with other network functions. It represents the IP address on which the NRF listens for incoming connections and requests.
bindingIPv4: 127.0.0.10
- “Port”: This attribute specifies the port number on which the NRF listens for incoming connections and requests from other network functions.
port: 8000
- “mcc”: The “mcc” attribute represents the Mobile Country Code assigned to the specific network operator or geographical area associated with the NRF. It helps identify the country or region to which the NRF belongs.
mcc: 208
- “mnc”: The “mnc” attribute stands for Mobile Network Code and represents the specific code assigned to the network operator within the defined country or region. It differentiates between different mobile network operators operating within the same country or region.
mnc: 93
Open the NRF configuration file and modify the mentioned attributes with their respective values.
vim ~/free5gc/config/nrfcfg.yaml
Tip: In vim, press “i” to enter insert mode and start editing. To save and exit, press the “esc” key followed by “:wq” and hit Enter.
Error generating access link