PDU Session – 2
PDU Session Establishment – Part 3
The following figure outlines the third part of the PDU session establishment:
(1) PDU Session Establishment Accept
Once interaction with the UDM, PCF and UPF has taken place successfully, the SMF can return the NAS PDU Session Establishment Accept to the device, via the AMF.
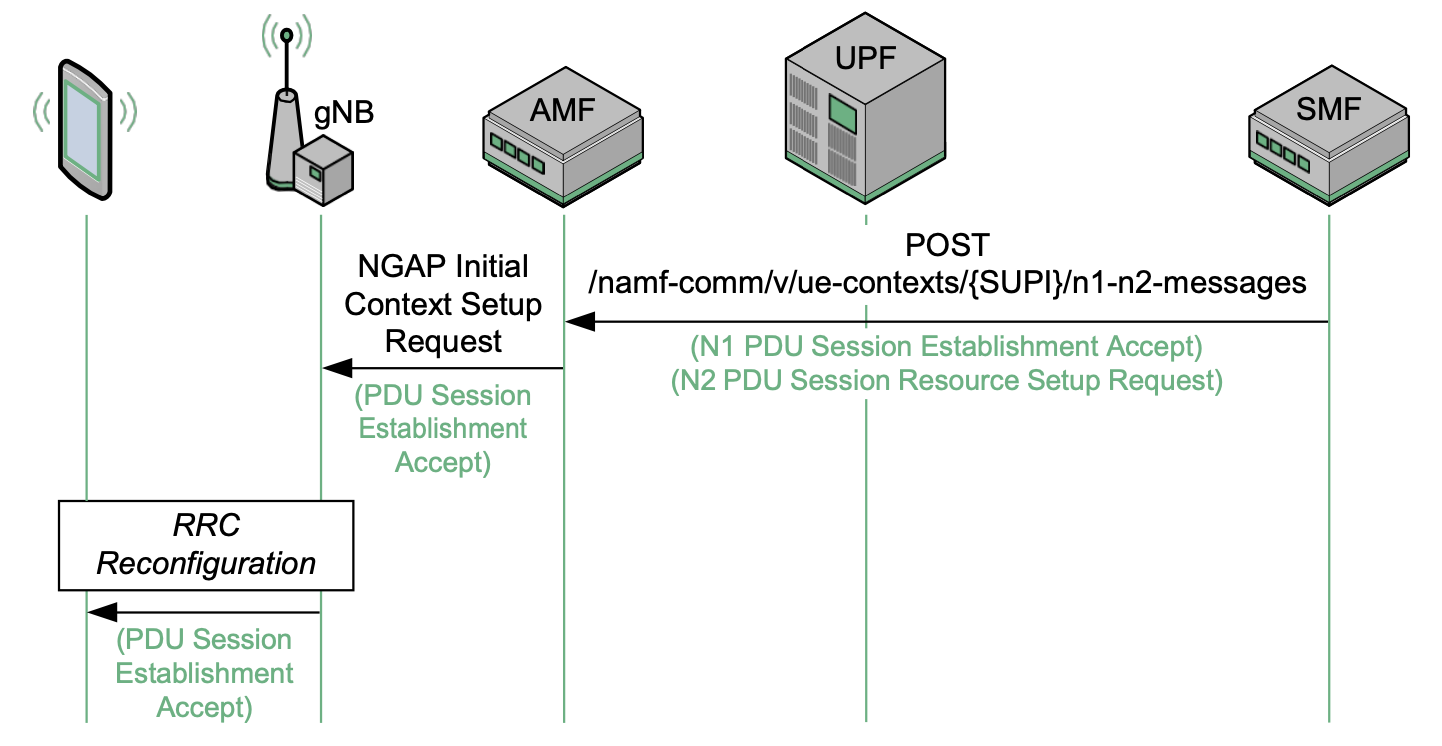
(2) NGAP Initial Context Setup Request
To allow the gNB to accommodate the subscriber, the NGAP Initial Context Setup Request message must be sent by the AMF to the gNB. The message contains the NAS PDU Session Establishment Accept (supplied by the SMF), along with the PDU Session Resource Setup Request IE (also provided by the SMF). This NGAP level information allows the gNB to establish radio network resources for the session, via the RRC Reconfiguration procedure.
(3) RRC Reconfiguration
Once the gNB receives the NGAP Initial Context Setup Request message, it is able to allocate radio resources to the device via the RRC Reconfiguration procedure.
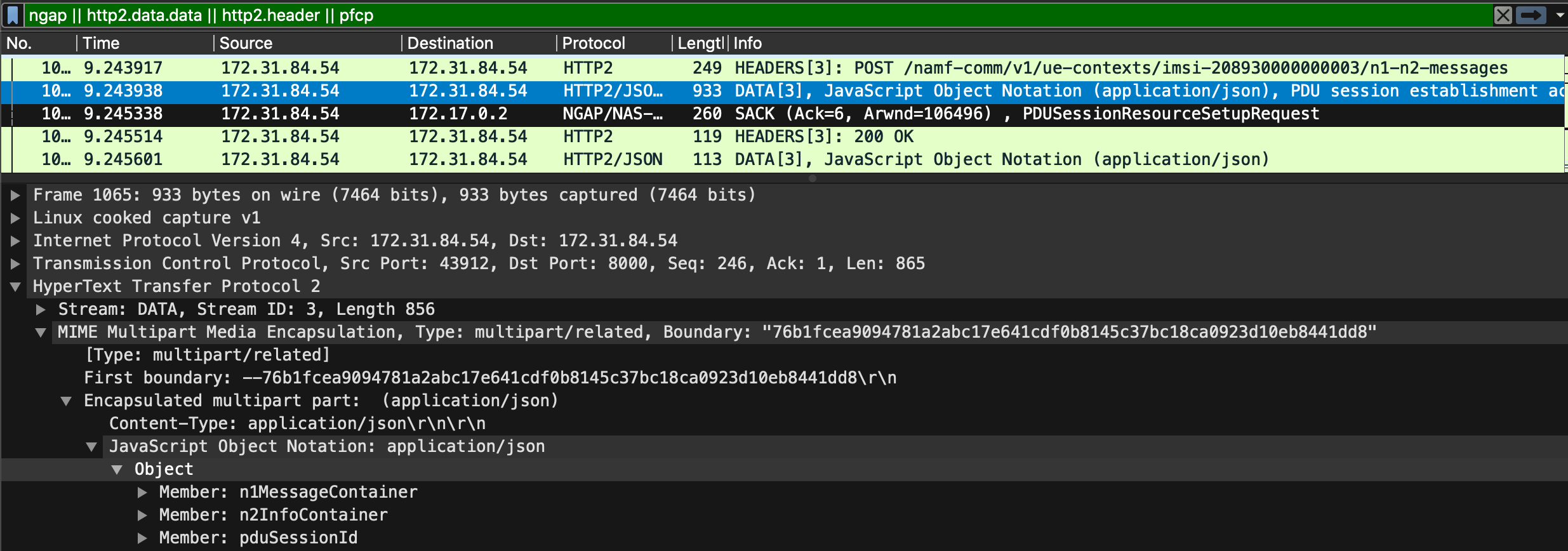
- The wireshark section correspond to this part :
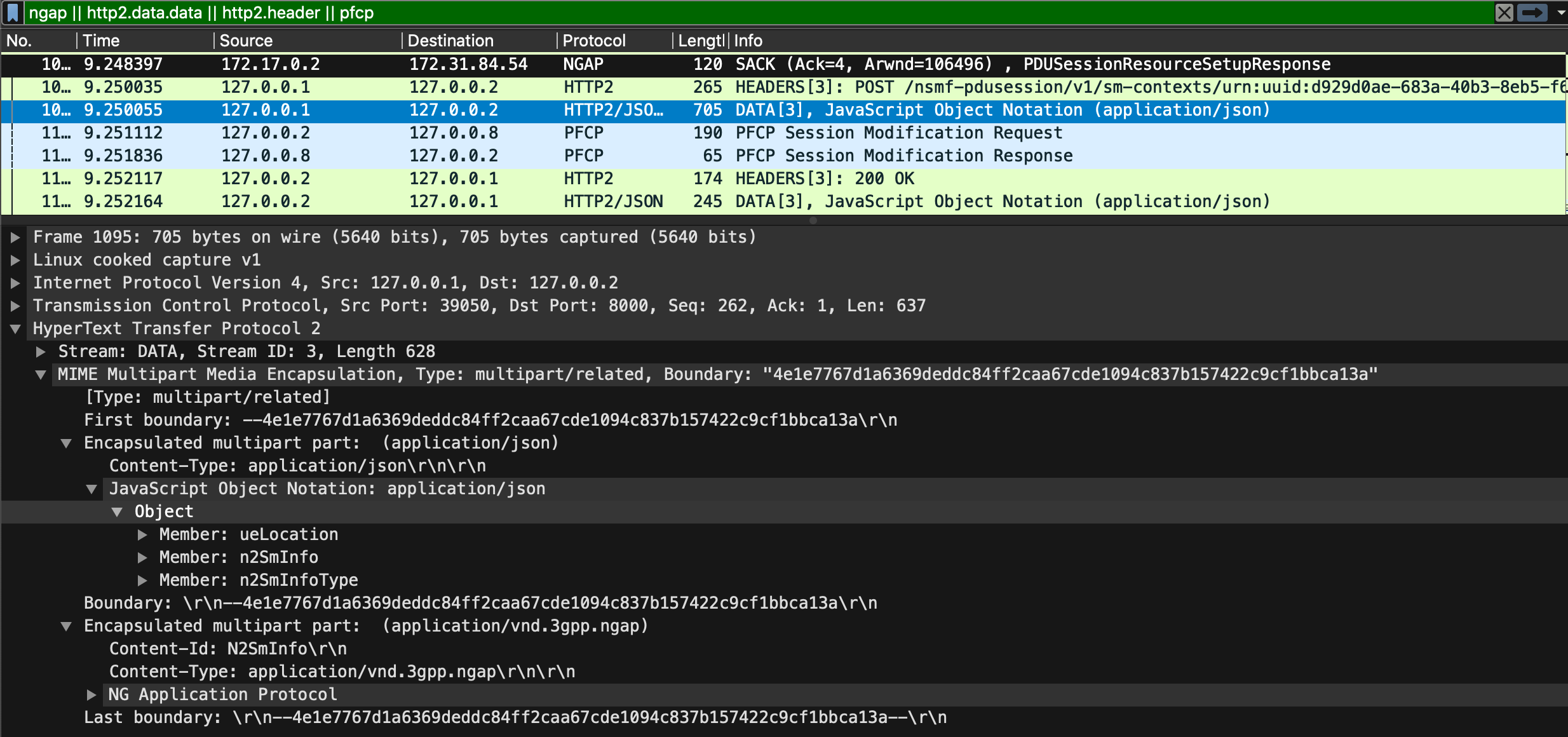
PDU Session Establishment – Part 4
The following figure outlines the last part of the PDU session establishment:
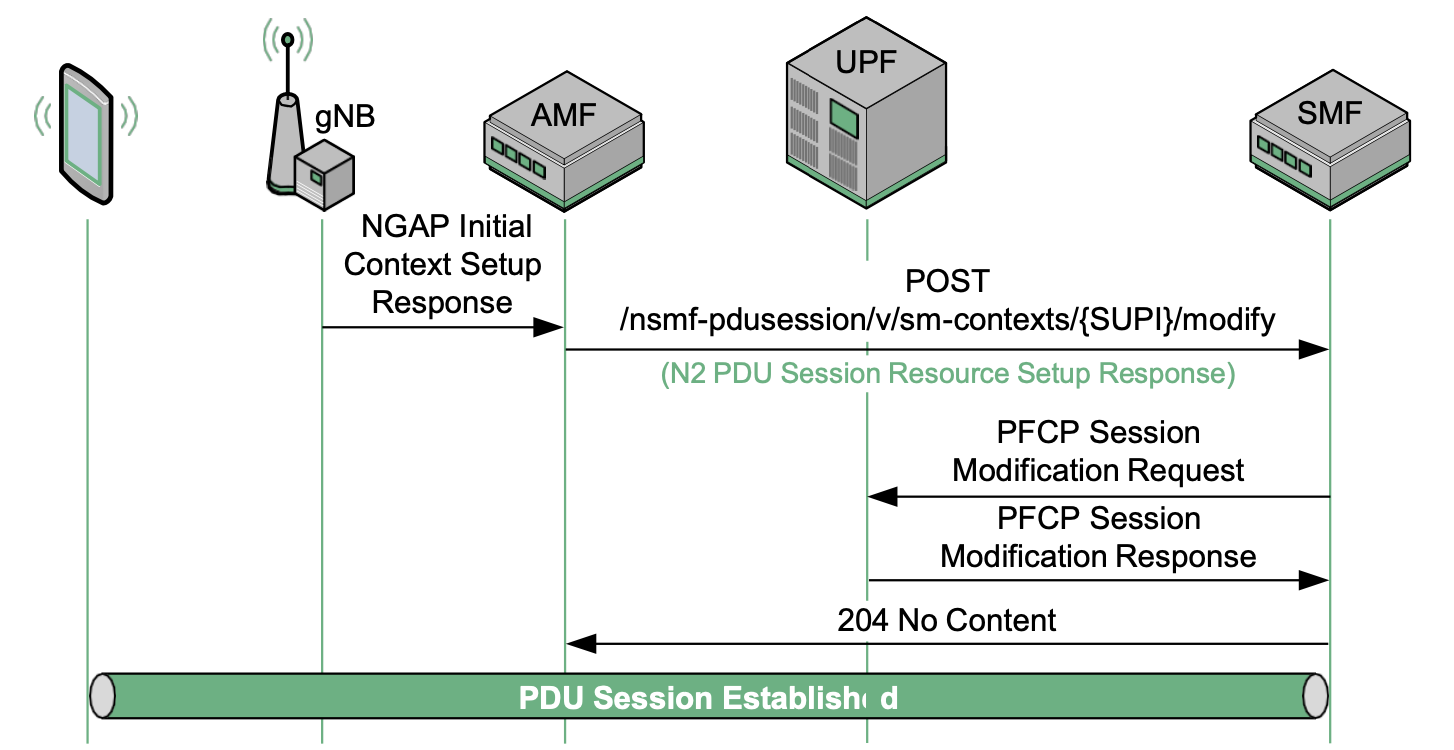
(1) NGAP Initial Context Setup Response
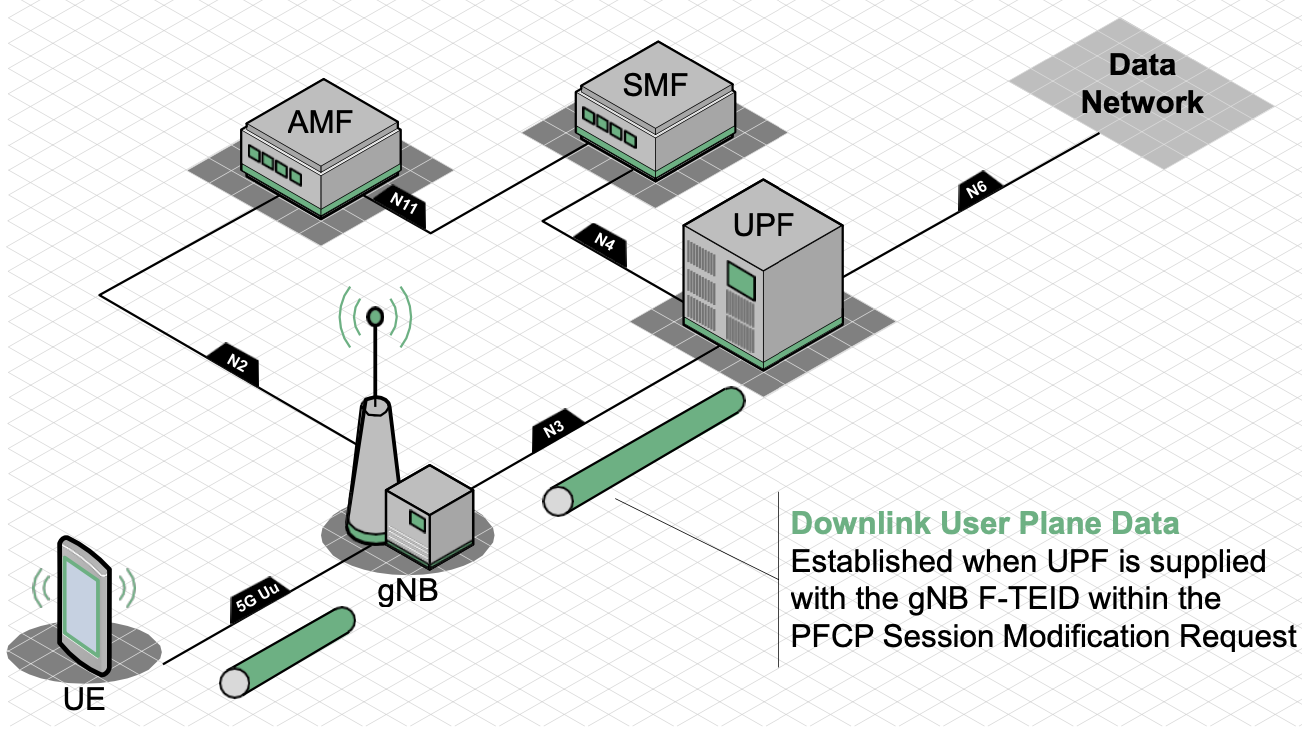
Assuming the PDU Session (QoS Flow) has been successfully established, this message will provide a confirmation to the AMF which includes the F-TEID of the gNB. This will ultimately be used by the UPF for forwarding downlink User Plane traffic.
(2) Finalizing the PDU Session
The remaining aspects of the PDU Session Establishment are largely related to conveying the gNB F-TEID to the UPF. To achieve this, a combination of the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContextRequest and PFCP Session Modification are used.
In response, the PFCP Session Modification Response and Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContextResponse are used to confirm that the modification has taken place. Once the UPF receives the gNB TEID in the PFCP Session Modification Request, the final element of User Plane connectivity is established. That is, the UPF now knows where to send User Plane traffic in the downlink direction.