5G Core Architecture
Introduction
5G is the latest standard in wireless communication technology, representing the fifth generation of mobile networks. It brings substantial improvements compared to previous generations. These advancements include higher data rates, reduced latency, increased capacity, and enhanced connectivity.
These upgrades enable a diverse range of applications to benefit from faster speeds, more responsive connections, and improved overall network performance.
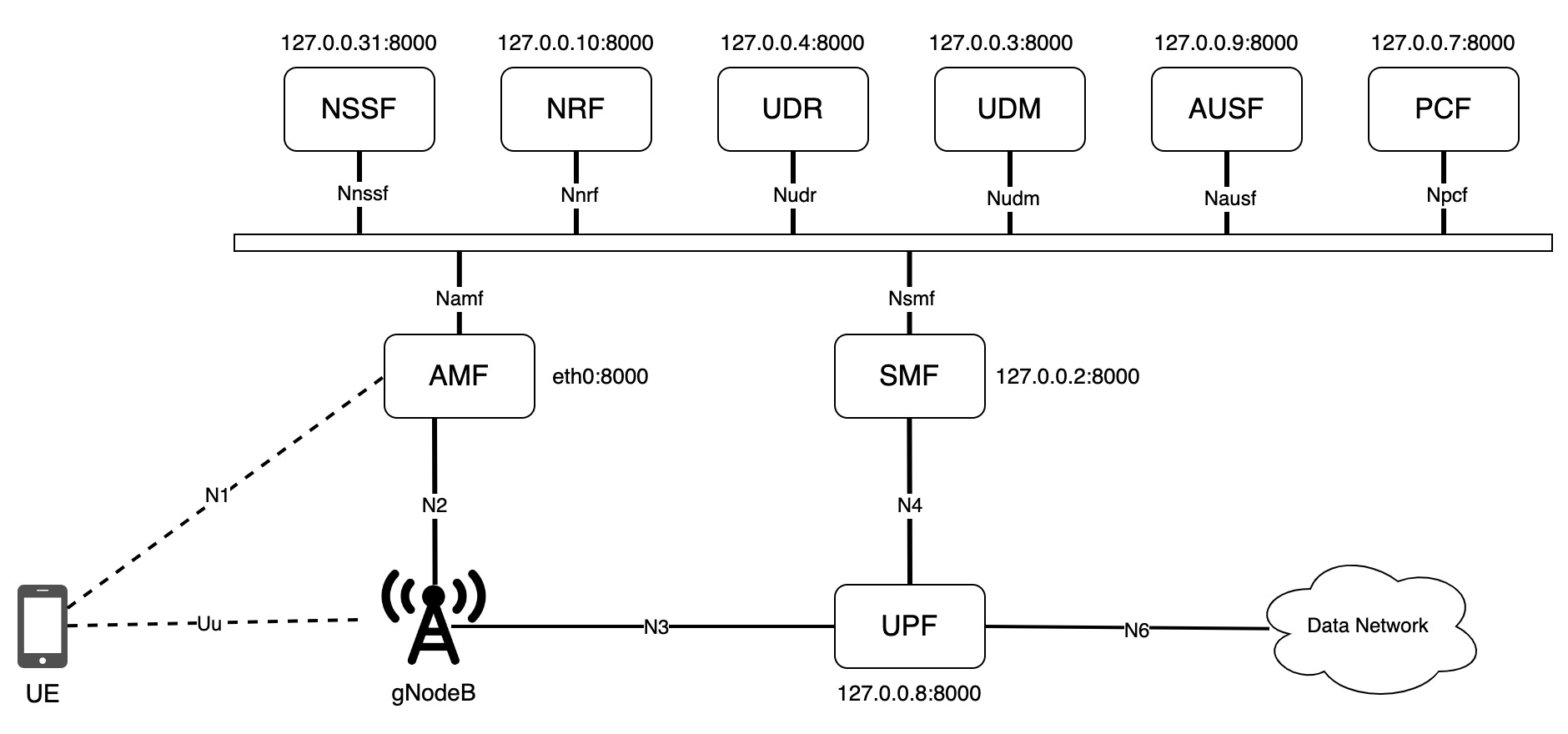
The following diagram illustrates various components comprising a complete 5G network.
The core network, which serves as a vital component within the 5G network, is built on the foundation of Service-Based Architecture (SBA).
Service Based Architecture
SBA provides a modular and flexible framework for the core network, enabling efficient service delivery and management.
In SBA, the core network is decomposed into smaller, self-contained entities called Network Functions (NFs). These NFs provide specific network services and are interconnected through standardized interfaces called SBIs. The two main components in SBA are:
- Network Functions (NFs): NFs are individual software modules or entities responsible for specific network functionalities, such as user authentication, mobility management, session management, or service discovery. Each NF performs a specific task and communicates with other NFs through well-defined APIs.
- Service-Based Interfaces (SBIs): SBIs are standardized interfaces that facilitate communication and interaction between different NFs within the service-based architecture.
NFs functions can act as service consumers or service providers, depending on their role in the network.
5G NFs Configuration
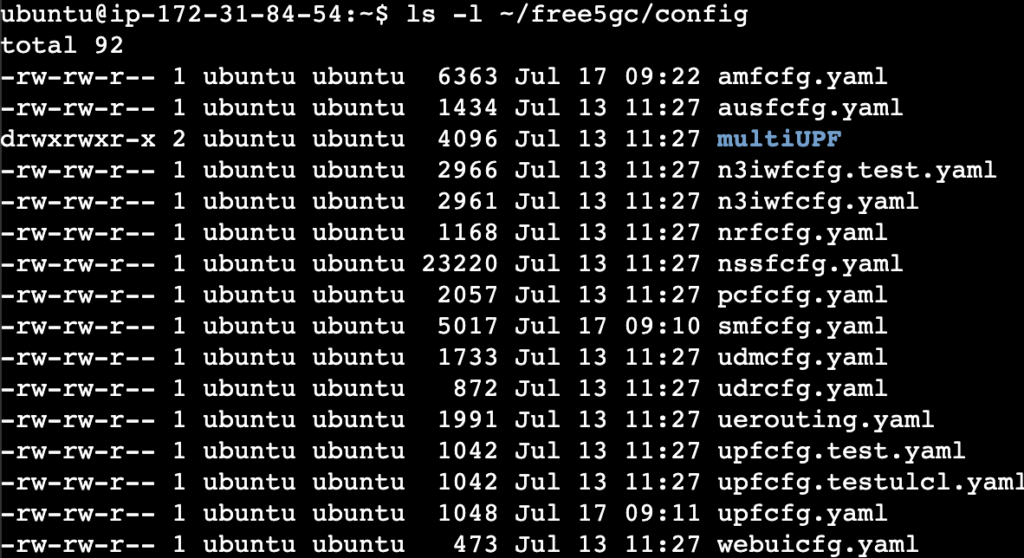
The following figure represents different 5G nodes installed on the LAB environment, in the next sections we will explore each node and perform the necessary configurations to establish seamless communication among the different network functions (NFs).
Note : the configuration process is crucial to ensure that the NFs can effectively and reliably communicate with each other since none of them have been pre-configured.
- The configuration files for various Network Functions (NFs) are located in the “~/free5gc/config” directory.
ls -l ~/free5gc/config
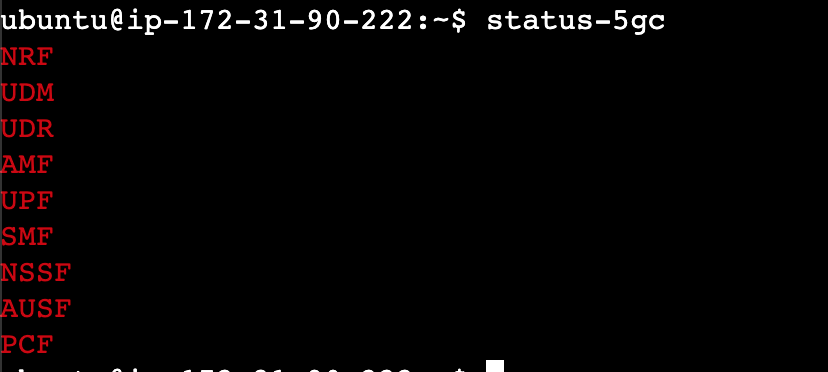
To view the status of the 5G core network, you can use the following command:
status-5gc
Note: The 5GC is considered inactive when all its displayed nodes are colored red.
To activate 5GC nodes, you need to configure them individually. Each node has an associated configuration file with some parameters left unconfigured, marked as “XXXXXX”, you must replace them in each configuration file with the specific values we provide for each node.